How Overvoltage Affects Solenoid Valves
Every solenoid valve has a nominal actuation voltage, which is usually based on common power supply voltages such as 12 VDC, 24 VDC, 110 VAC, or 220 VAC. The nominal voltage is typically printed somewhere on the valve body or coil and is the voltage required to actuate (shift) the valve. Applying less than the nominal voltage will result in undervoltage and may result in a slower "on" response time or the valve not actuating at all. Applying more than the nominal voltage will result in overvoltage, which can result in a faster "on" response time of a valve. However, extreme overvoltage could permanently damage the coil.
Nominal vs. Rated Voltage
Most solenoid valves also have a rated voltage range, such as +/- 10% of the nominal voltage. For example, a 12 VDC +/- 10% rated voltage would allow between 10.8 VDC and 13.2 VDC to be applied to a solenoid and still achieve normal operation for the valve.
Pros & Cons of Solenoid Valve Overvoltage
Some customers will intentionally overvoltage solenoid valves while remaining within the rated voltage range in order to get a faster "on" response time. While this will not damage the solenoid, there are a few things to understand when doing this.
BENEFITS:
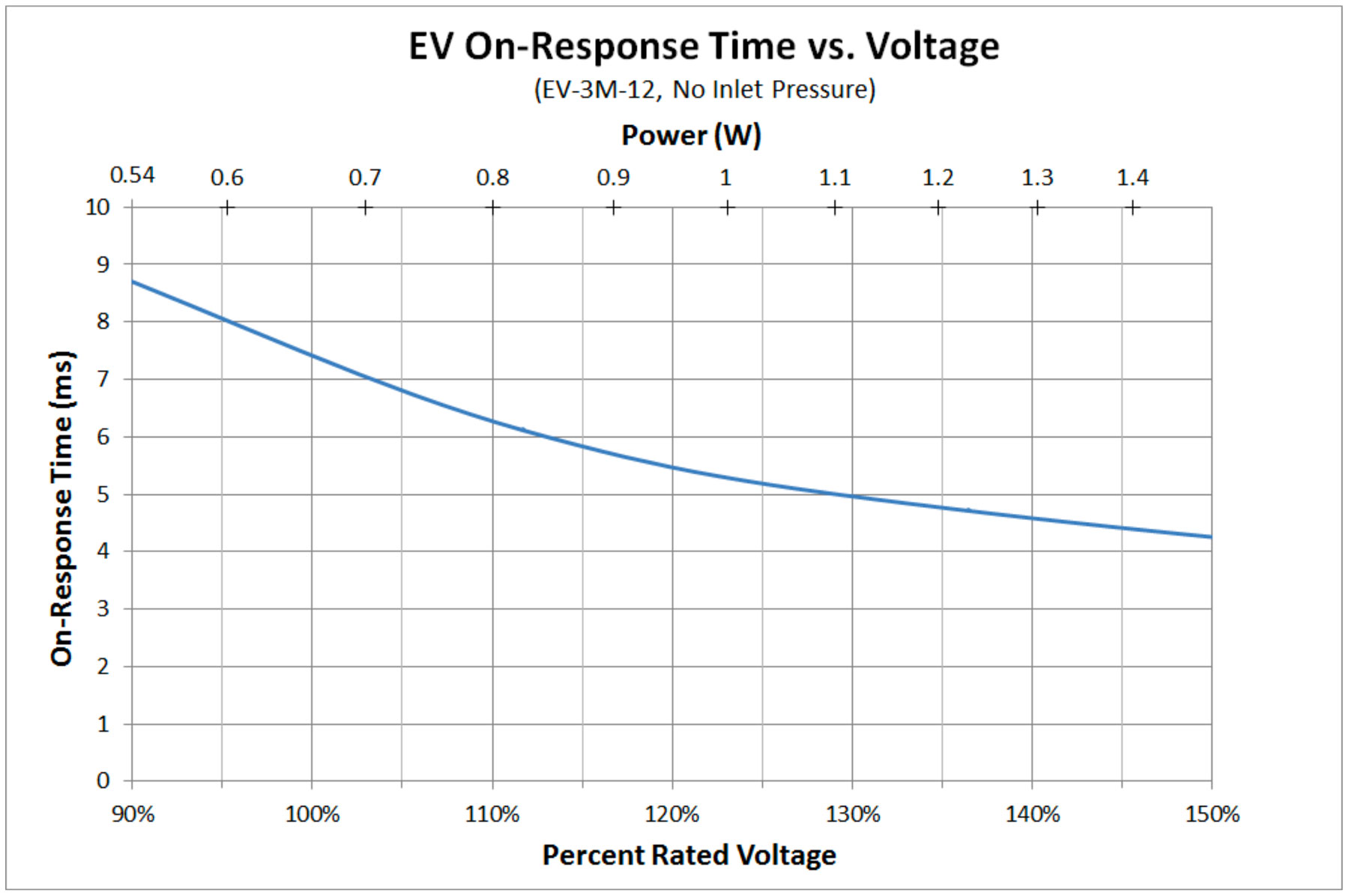
- "On" response time will decrease as voltage is increased (see Chart 1).
DRAWBACKS:
- "Off" response time will increase as voltage is increased.
- Power required will increase as voltage is increased (see Chart 1).
- Due to increased power usage, heat generation will also increase.
ĐÇłÇweb Valves & Overvoltage
Many of ĐÇłÇweb's valves actually allow a significant overvoltage. Our , for instance, are rated for 90-150% of the nominal voltage (Table 1), as are our (Table 2). Our are rated for 95-125% of the nominal voltage (Table 3) and our are rated for 100-120% of the nominal voltage (Table 4). This allows customers to get faster "on" response times if their application requires it.
Ěý
|
Table 1
EV / ET Coil Rated Voltage Ranges |
Ěý |
Table 2
2013 Coil Rated Voltage Ranges |
||
| Solenoid | Working Range | Ěý | Solenoid | Working Range |
| 0.8 VDC | 0.7 - 1.2 VDC | Ěý | 6 VDC | 5.4 - 9.0 VDC |
| 1.4 VDC | 1.3 - 2.1 VDC | Ěý | 12 VDC | 10.8 - 18.0 VDC |
| 3 VDC | 2.7 - 4.5 VDC | Ěý | 24 VDC | 21.5 - 36.0 VDC |
| 5 VDC | 4.5 - 7.5 VDC | Ěý | Ěý | Ěý |
| 5.7 VDC | 5.1 - 8.5 VDC | Ěý | Ěý | Ěý |
| 6 VDC | 5.4 - 9.0 VDC | Ěý | Ěý | Ěý |
| 9 VDC | 8.1 - 14.0 VDC | Ěý | Ěý | Ěý |
| 12 VDC | 10.8 - 18.0 VDC | Ěý | Ěý | Ěý |
| 15.5 VDC | 14.0 - 23.0 VDC | Ěý | Ěý | Ěý |
| 18 VDC | 16.0 - 27.0 VDC | Ěý | Ěý | Ěý |
| 24 VDC | 21.5 - 36.0 VDC | Ěý | Ěý | Ěý |
| Ěý | ||||
|
Table 3
DV Coil Rated Voltage Ranges |
Ěý |
Table 4
NIV Coil Rated Voltage Ranges |
||
| Solenoid | Working Range | Ěý | Solenoid | Working Range |
| 12 VDC | 11.4 - 15.0 VDC | Ěý | 12 VDC | 12.0 - 14.4 VDC |
| 24 VDC | 22.8 - 30.0 VDC | Ěý | 24 VDC | 24.0 - 28.8 VDC |
| Ěý | Ěý | Ěý | Ěý | Ěý |
Ěý
Ěý
Ěý
Ěý
Ěý
Ěý
Ěý
Ěý